SpringBoot 在 IDEA 中实现热部署
1、开启 IDEA 的自动编译(静态)
具体步骤:打开顶部工具栏 File -> Settings -> Default Settings -> Build -> Compiler 然后勾选 Build project automatically 。
2、开启 IDEA 的自动编译(动态)
具体步骤:同时按住 Ctrl + Shift + Alt + / 然后进入 Registry ,勾选自动编译并调整延时参数。
- compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running -> 自动编译
- compile.document.save.trigger.delay -> 自动更新文件
PS:网上极少有人提到 compile.document.save.trigger.delay 它主要是针对静态文件如 JS CSS 的更新,将延迟时间减少后,直接按 F5 刷新页面就能看到效果!
3、开启 IDEA 的热部署策略(非常重要)
具体步骤:顶部菜单- >Edit Configurations->SpringBoot 插件->目标项目->勾选热更新。
4、在项目添加热部署插件(可选)
温馨提示:
如果因为旧项目十分臃肿,导致每次都自动热重启很慢而影响开发效率,笔者建议直接在 POM 移除spring-boot-devtools依赖,然后使用 Control+Shift+F9 进行手工免启动快速更新!!
具体步骤:在 POM 文件添加热部署插件
5、关闭浏览器缓存(重要)
打开谷歌浏览器,打开 F12 的 Network 选项栏,然后勾选【✅】Disable cache 。
SpringBoot 全局异常处理
在 SpringBoot 项目中,由于我们项目中难免会出现各种异常,一个个处理并不一定能包括全部异常,这时候我们需要一个全局类来处理项目中所抛出的异常。
@ControllerAdvice 注解的三种使用场景
@ControllerAdvice ,很多初学者可能都没有听说过这个注解,实际上,这是一个非常有用的注解,顾名思义,这是一个增强的 Controller。使用这个 Controller ,可以实现三个方面的功能:
- 全局异常处理
- 全局数据绑定
- 全局数据预处理
灵活使用这三个功能,可以帮助我们简化很多工作,需要注意的是,这是 SpringMVC 提供的功能,在 Spring Boot 中可以直接使用,下面分别来看。
全局异常处理
使用 @ControllerAdvice 实现全局异常处理,只需要定义类,添加该注解即可定义方式如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyGlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ModelAndView customException(Exception e) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("message", e.getMessage());
mv.setViewName("myerror");
return mv;
}
}在该类中,可以定义多个方法,不同的方法处理不同的异常,例如专门处理空指针的方法、专门处理数组越界的方法…,也可以直接向上面代码一样,在一个方法中处理所有的异常信息。
@ExceptionHandler 注解用来指明异常的处理类型,即如果这里指定为 NullpointerException,则数组越界异常就不会进到这个方法中来。
全局数据绑定
全局数据绑定功能可以用来做一些初始化的数据操作,我们可以将一些公共的数据定义在添加了 @ControllerAdvice 注解的类中,这样,在每一个 Controller 的接口中,就都能够访问导致这些数据。
使用步骤,首先定义全局数据,如下:
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyGlobalExceptionHandler {
@ModelAttribute(name = "md")
public Map<String,Object> mydata() {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age", 99);
map.put("gender", "男");
return map;
}
}使用 @ModelAttribute 注解标记该方法的返回数据是一个全局数据,默认情况下,这个全局数据的 key 就是返回的变量名,value 就是方法返回值,当然开发者可以通过 @ModelAttribute 注解的 name 属性去重新指定 key。
定义完成后,在任何一个 Controller 的接口中,都可以获取到这里定义的数据:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model) {
Map<String, Object> map = model.asMap();
System.out.println(map);
int i = 1 / 0;
return "hello controller advice";
}
}全局数据预处理
考虑我有两个实体类,Book 和 Author,分别定义如下:
@Data
public class Book {
private String name;
private Long price;
}
@Data
public class Author {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}此时,如果我定义一个数据添加接口,如下:
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(Book book, Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}这个时候,添加操作就会有问题,因为两个实体类都有一个 name 属性,从前端传递时 ,无法区分。此时,通过 @ControllerAdvice 的全局数据预处理可以解决这个问题
解决步骤如下: 1.给接口中的变量取别名
@PostMapping("/book")
public void addBook(@ModelAttribute("b") Book book, @ModelAttribute("a") Author author) {
System.out.println(book);
System.out.println(author);
}2.进行请求数据预处理
在 @ControllerAdvice 标记的类中添加如下代码:
@InitBinder("b")
public void b(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("b.");
}
@InitBinder("a")
public void a(WebDataBinder binder) {
binder.setFieldDefaultPrefix("a.");
}@InitBinder(“b”) 注解表示该方法用来处理和 Book 和相关的参数,在方法中,给参数添加一个 b 前缀,即请求参数要有 b 前缀. 3.发送请求
请求发送时,通过给不同对象的参数添加不同的前缀,可以实现参数的区分.
基本用法
定义一个全局异常配置类:
import com.ck.syscheck.utils.JsonResult;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeMismatchException;
import org.springframework.beans.ConversionNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotWritableException;
import org.springframework.web.HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 定义全局异常类
*/
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private static final String logExceptionFormat = "Capture Exception By GlobalExceptionHandler: Code: %s Detail: %s";
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 运行时异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public String runtimeExceptionHandler(RuntimeException ex) {
return resultFormat(1, ex);
}
/**
* 空指针异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NullPointerException.class)
public String nullPointerExceptionHandler(NullPointerException ex) {
System.err.println("NullPointerException:");
return resultFormat(2, ex);
}
/**
* 类型转换异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ClassCastException.class)
public String classCastExceptionHandler(ClassCastException ex) {
return resultFormat(3, ex);
}
/**
* IO异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(IOException.class)
public String iOExceptionHandler(IOException ex) {
return resultFormat(4, ex);
}
/**
* 未知方法异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(NoSuchMethodException.class)
public String noSuchMethodExceptionHandler(NoSuchMethodException ex) {
return resultFormat(5, ex);
}
/**
* 数组越界异常
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public String indexOutOfBoundsExceptionHandler(IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
return resultFormat(6, ex);
}
/**
* 400错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({HttpMessageNotReadableException.class})
public String requestNotReadable(HttpMessageNotReadableException ex) {
System.out.println("400..requestNotReadable");
return resultFormat(7, ex);
}
/**
* 400错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({TypeMismatchException.class})
public String requestTypeMismatch(TypeMismatchException ex) {
System.out.println("400..TypeMismatchException");
return resultFormat(8, ex);
}
/**
* 400错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({MissingServletRequestParameterException.class})
public String requestMissingServletRequest(MissingServletRequestParameterException ex) {
System.out.println("400..MissingServletRequest");
return resultFormat(9, ex);
}
/**
* 405错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class})
public String request405(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException ex) {
return resultFormat(10, ex);
}
/**
* 406错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class})
public String request406(HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {
System.out.println("406...");
return resultFormat(11, ex);
}
/**
* 500错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({ConversionNotSupportedException.class, HttpMessageNotWritableException.class})
public String server500(RuntimeException ex) {
System.out.println("500...");
return resultFormat(12, ex);
}
/**
* 栈溢出
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({StackOverflowError.class})
public String requestStackOverflow(StackOverflowError ex) {
return resultFormat(13, ex);
}
/**
* 除数不能为0
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({ArithmeticException.class})
public String arithmeticException(ArithmeticException ex) {
return resultFormat(13, ex);
}
/**
* 其他错误
*
* @param ex
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class})
public String exception(Exception ex) {
return resultFormat(14, ex);
}
/**
* 格式化结构,将其转换为JSon格式
* 这里使用alibaba的fastjson依赖
*
* @param code
* @param ex
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
private <T extends Throwable> String resultFormat(Integer code, T ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
log.error(String.format(logExceptionFormat, code, ex.getMessage()));
return JsonResult.failed(code, ex.getMessage());
}
}JsonResult 是前后端分离数据交互格式
@Data
public class JsonResult implements Serializable {
/**
* 返回码 非0即失败
*/
private int code;
/**
* 消息提示
*/
private String msg;
/**
* 返回的数据
*/
private Map<String, Object> data;
public JsonResult() {
}
public JsonResult(int code, String msg, Map<String, Object> data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
public static String success() {
return success(new HashMap(0));
}
public static String success(Map<String, Object> data) {
return JSON.toJSONString(new JsonResult(0, "解析成功", data));
}
public static String failed() {
return failed("解析失败");
}
public static String failed(String msg) {
return failed(-1, msg);
}
public static String failed(int code, String msg) {
return JSON.toJSONString(new JsonResult(code, msg, new HashMap(0)));
}
}必要注解:@ControllerAdvice: _@ControllerAdvice__ 是对 Controller 的增强,不用任何的配置,只要把这个类放在项目中,Spring 能扫描到的地方。就可以实现全局异常的回调。_
@ControllerAdvice 是@Component 注解的一个延伸注解,Spring 会自动扫描并检测被@ControllerAdvice 所标注的类。
@ControllerAdvice 可以和@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder 以及@ModelAttribute 注解搭配使用,主要是用来处理控制器所抛出的异常信息。
首先,我们需要定义一个被@ControllerAdvice 所标注的类,在该类中,定义一个用于处理具体异常的方法,并使用@ExceptionHandler 注解进行标记。
此外,在有必要的时候,可以使用@InitBinder 在类中进行全局的配置,还可以使用@ModelAttribute 配置与视图相关的参数。使用@ControllerAdvice 注解,就可以快速的创建统一的,自定义的异常处理类。
SpringBoot 中@ControllerAdvice 结合@InitBinder、@ModelAttribute、@ExceptionHandler 的使用参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/backbug/article/details/105317630
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
}高级用法
参考开源项目 RuoYi,看看它的全局异常处理是怎么搞的
https://github.com/yangzongzhuan/RuoYi
定义错误页面
RuoYi\ruoyi-admin\src\main\resources\templates\error\404.html
全局异常处理类
RuoYi\ruoyi-framework\src\main\java\com\ruoyi\framework\web\exception\GlobalExceptionHandler.java:
package com.ruoyi.framework.web.exception;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import com.ruoyi.common.core.domain.AjaxResult;
import com.ruoyi.common.exception.BusinessException;
import com.ruoyi.common.exception.DemoModeException;
import com.ruoyi.common.utils.ServletUtils;
import com.ruoyi.common.utils.security.PermissionUtils;
/**
* 全局异常处理器
*
* @author ruoyi
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler
{
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 权限校验失败 如果请求为ajax返回json,普通请求跳转页面
*/
@ExceptionHandler(AuthorizationException.class)
public Object handleAuthorizationException(HttpServletRequest request, AuthorizationException e)
{
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
if (ServletUtils.isAjaxRequest(request))
{
return AjaxResult.error(PermissionUtils.getMsg(e.getMessage()));
}
else
{
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("error/unauth");
return modelAndView;
}
}
/**
* 请求方式不支持
*/
@ExceptionHandler({ HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class })
public AjaxResult handleException(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e)
{
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return AjaxResult.error("不支持' " + e.getMethod() + "'请求");
}
/**
* 拦截未知的运行时异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public AjaxResult notFount(RuntimeException e)
{
log.error("运行时异常:", e);
return AjaxResult.error("运行时异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 系统异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public AjaxResult handleException(Exception e)
{
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return AjaxResult.error("服务器错误,请联系管理员");
}
/**
* 业务异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
public Object businessException(HttpServletRequest request, BusinessException e)
{
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
if (ServletUtils.isAjaxRequest(request))
{
return AjaxResult.error(e.getMessage());
}
else
{
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("errorMessage", e.getMessage());
modelAndView.setViewName("error/business");
return modelAndView;
}
}
/**
* 自定义验证异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public AjaxResult validatedBindException(BindException e)
{
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
String message = e.getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage();
return AjaxResult.error(message);
}
/**
* 演示模式异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(DemoModeException.class)
public AjaxResult demoModeException(DemoModeException e)
{
return AjaxResult.error("演示模式,不允许操作");
}
}前后端数据交互 AjaxResult
public class AjaxResult extends HashMap<String, Object>
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/** 状态码 */
public static final String CODE_TAG = "code";
/** 返回内容 */
public static final String MSG_TAG = "msg";
/** 数据对象 */
public static final String DATA_TAG = "data";
/**
* 状态类型
*/
public enum Type
{
/** 成功 */
SUCCESS(0),
/** 警告 */
WARN(301),
/** 错误 */
ERROR(500);
private final int value;
Type(int value)
{
this.value = value;
}
public int value()
{
return this.value;
}
}
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象,使其表示一个空消息。
*/
public AjaxResult()
{
}
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象
*
* @param type 状态类型
* @param msg 返回内容
*/
public AjaxResult(Type type, String msg)
{
super.put(CODE_TAG, type.value);
super.put(MSG_TAG, msg);
}
/**
* 初始化一个新创建的 AjaxResult 对象
*
* @param type 状态类型
* @param msg 返回内容
* @param data 数据对象
*/
public AjaxResult(Type type, String msg, Object data)
{
super.put(CODE_TAG, type.value);
super.put(MSG_TAG, msg);
if (StringUtils.isNotNull(data))
{
super.put(DATA_TAG, data);
}
}
/**
* 方便链式调用
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return 数据对象
*/
@Override
public AjaxResult put(String key, Object value)
{
super.put(key, value);
return this;
}
/**
* 返回成功消息
*
* @return 成功消息
*/
public static AjaxResult success()
{
return AjaxResult.success("操作成功");
}
/**
* 返回成功数据
*
* @return 成功消息
*/
public static AjaxResult success(Object data)
{
return AjaxResult.success("操作成功", data);
}
/**
* 返回成功消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @return 成功消息
*/
public static AjaxResult success(String msg)
{
return AjaxResult.success(msg, null);
}
/**
* 返回成功消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @param data 数据对象
* @return 成功消息
*/
public static AjaxResult success(String msg, Object data)
{
return new AjaxResult(Type.SUCCESS, msg, data);
}
/**
* 返回警告消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @return 警告消息
*/
public static AjaxResult warn(String msg)
{
return AjaxResult.warn(msg, null);
}
/**
* 返回警告消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @param data 数据对象
* @return 警告消息
*/
public static AjaxResult warn(String msg, Object data)
{
return new AjaxResult(Type.WARN, msg, data);
}
/**
* 返回错误消息
*
* @return
*/
public static AjaxResult error()
{
return AjaxResult.error("操作失败");
}
/**
* 返回错误消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @return 警告消息
*/
public static AjaxResult error(String msg)
{
return AjaxResult.error(msg, null);
}
/**
* 返回错误消息
*
* @param msg 返回内容
* @param data 数据对象
* @return 警告消息
*/
public static AjaxResult error(String msg, Object data)
{
return new AjaxResult(Type.ERROR, msg, data);
}
}SpringBoot 加载顺序

_@_Order(num) //加载顺序 num 数字越小 优先级越高
加载顺序打印
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM warning: Options -Xverify:none and -noverify were deprecated in JDK 13 and will likely be removed in a future release.
The service to start.
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.4.3)
2022-02-08 11:00:34.993 INFO 13164 --- [ main] com.neo.CommandLineRunnerApplication :
...
2022-02-08 11:00:36.407 INFO 13164 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
2022-02-08 11:00:36.419 INFO 13164 --- [ main] com.neo.CommandLineRunnerApplication : Started CommandLineRunnerApplication in 1.929 seconds (JVM running for 3.343)
The OrderRunner1 start to initialize ...
The OrderRunner2 start to initialize ...
The Runner start to initialize ...
The service has started.SpringBoot 自动装配原理
https://www.cnblogs.com/hellokuangshen/p/12468522.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42025798/article/details/122058013
【狂神说 Java】SpringBoot 最新教程 IDEA 版通俗易懂
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42025798/article/details/121974573
【狂神说 Java 笔记】Java 后端开发工程师学习笔记
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42025798/article/details/119192030
03-SpringBoot 源码分析
VBlog 上传到 GitHub 项目
https://github.com/lenve/VBlog
vue 项目不上传的文件和目录
springboot 项目不上传的文件和文件夹
SpringBoot 事务管理
SpringBoot 使用事务非常简单,底层依然采用的是 Spring 本身提供的事务管理
• 在入口类中使用注解 @EnableTransactionManagement 开启事务支持
• 在访问数据库的 Service 方法上添加注解 _@_Transactional 即可
案例思路
通过 SpringBoot +MyBatis 实现对数据库学生表的更新操作,在 service 层的方法中构建异常,查看事务是否生效;
实现步骤
1)在 StudentController 中添加更新学生的方法
@Controller
public class SpringBootController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/springBoot/update")
public @ResponseBody Object update() {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1);
student.setName("Mark");
student.setAge(100);
int updateCount = studentService.update(student);
return updateCount;
}
}2)在 StudentService 接口中添加更新学生方法
public interface StudentService {
int update(Student student);
}3)在 StudentServiceImpl 接口实现类中对更新学生方法进行实现,并构建一个异常,同时在该方法上加@Transactional 注解
@Override
@Transactional //添加此注解说明该方法添加的事务管理
public int update(Student student) {
int updateCount = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(student);
System.out.println("更新结果:" + updateCount);
//在此构造一个除数为0的异常,测试事务是否起作用
int a = 10/0;
return updateCount;
}4)在 Application 类上加@EnableTransactionManagement 开启事务支持
@EnableTransactionManagement 可选,但是@Service 必须添加事务才生效
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement //SpringBoot开启事务的支持
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}5)启动 Application,通过浏览器访问进行测试
浏览器
IDEA 控制台
数据库表
通过以上结果,说明事务起作用了。
6)注释掉 StudentServiceImpl 上的@Transactional 测试
数据库的数据被更新
Spring 全家桶注解汇总
40 个 常用的 Sprin 链接 gBoot 注解,你知道几个?[
](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ijPn2-q7hxFw-G8KYrmghg)
SpringBoot 常用注解大全,一目了然!
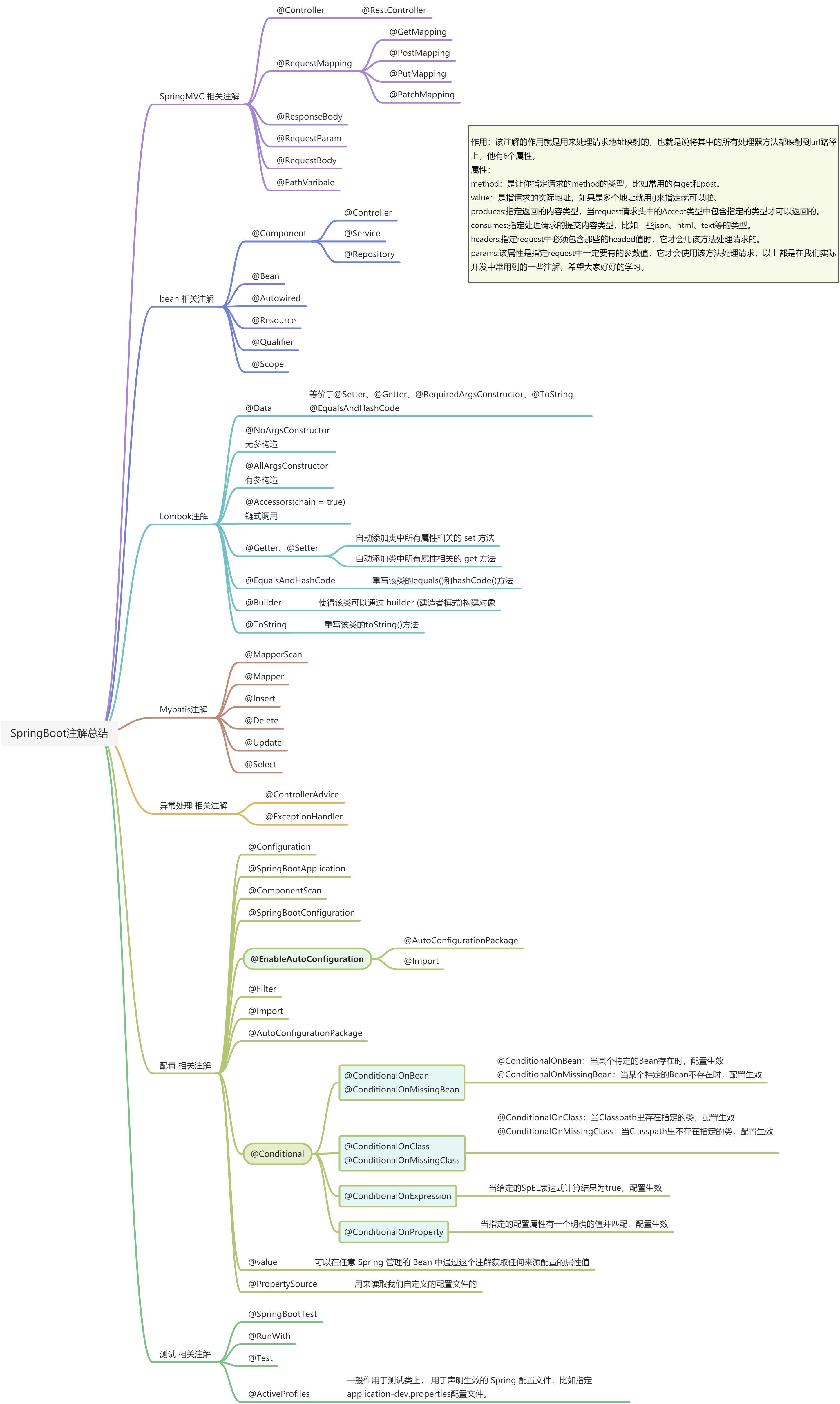
SpringMVC 相关注解
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/cjeandailynotes/p/10469377.html
SpringBoot 中的 SpringMVC 和之前的 SpringMVC 框架使用是完全一样的,主要有以下注解:
_@_Controller
SpringMVC 的注解,处理 http 请求,一般放在 xxxController.java , 类的上面
_@_RestController
Spring4 后新增注解,是@Controller 注解功能的增强,是@Controller + @ResponseBody 的组合注解;
如果一个 Controller 类添加了@RestController,那么该 Controller 类下的所有方法都相当于添加了@ResponseBody 注解;
用于返回字符串或 json 数据。
_@_RequestMapping
RequestMapping 是一个用来处理请求地址映射的注解(将请求映射到对应的控制器方法中),可用于类或方法上。
用于类上,表示类中的所有响应请求的方法都是以该地址作为父路径。
标注在方法上,表示那个具体的方法来接受处理某次请求。
Spring MVC 和 Spring WebFlux 都通过 RquestMappingHandlerMapping 和 RequestMappingHndlerAdapter 两个类来提供对@RequestMapping 注解的支持。
@RequestMapping 注解对请求处理类中的请求处理方法进行标注;@RequestMapping 注解拥有以下的六个配置属性:
- value:映射的请求 URL 或者其别名
- method:兼容 HTTP 请求方法名(默认是 get 请求)
- params:根据 HTTP 参数的存在、缺省或值对请求进行过滤
- header:根据 HTTP Header 的存在、缺省或值对请求进行过滤
- consume:设定在 HTTP 请求正文中允许使用的媒体类型
- product:在 HTTP 响应体中允许使用的媒体类型
提示:在使用@RequestMapping 之前,请求处理类还需要使用@Controller 或@RestController 进行标记
下面是使用@RequestMapping 的示例:
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/book")
public class BookController {
@RequestMapping(value="/title")
public String getTitle(){
return "title";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/content")
public String getContent(){
return "content";
}
}由于 BookController 类加了 value=”/book”的@RequestMapping 的注解,所以相关路径都要加上”/book”,即请求的 url 分别为:
(1)http://localhost:8080/book/title
(2)http://localhost:8080/book/content
“@RequestMapping”的 value 值前后是否有“/”对请求的路径没有影响,即 value=”book” 、”/book”、”/book/“其效果是一样的。
SpringMVC 提供了常用的请求方法注解,即指定请求方法的_@_RequestMapping
_@_GetMapping
RequestMapping 和 Get 请求方法的组合只支持 Get 请求;Get 请求主要用于查询操作。
_@_PostMapping
RequestMapping 和 Post 请求方法的组合只支持 Post 请求;Post 请求主要用户新增数据。
_@_PutMapping
RequestMapping 和 Put 请求方法的组合只支持 Put 请求;Put 通常用于修改数据。
_@_DeleteMapping
RequestMapping 和 Delete 请求方法的组合只支持 Delete 请求;通常用于删除数据。
@RequestMapping()的所有属性:
//这三个参数是一样的,都是匹配路由
String name() default "";
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
//请求方法
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
//@RequestMapping(value = "/hello",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//请求参数
String[] params() default {};
//请求头
String[] headers() default {};
//@RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*")
//will match requests with a Content-Type of "text/html", "text/plain", etc
String[] consumes() default {};
String[] produces() default {};value:指定请求的实际 url
(1)普通的具体值
如 value=”/book”。
(2)含某变量的一类值
@RequestMapping(value="/get/{bookId}")
public String getBookById(@PathVariable String bookId,Model model){
model.addAttribute("bookId", bookId);
return "book";
}路径中的 bookId 可以当变量,@PathVariable 注解即提取路径中的变量值。
(3)ant 风格
//可匹配“/get/id1”或“/get/ida”,但不匹配“/get/id”或“/get/idaa”;
@RequestMapping(value="/get/id?")
//可匹配“/get/idabc”或“/get/id”,但不匹配“/get/idabc/abc”;
@RequestMapping(value="/get/id*")
//可匹配“/get/id/abc”,但不匹配“/get/idabc”;
@RequestMapping(value="/get/id/*")
//可匹配“/get/id/abc/abc/123”或“/get/id/123”,也就是Ant风格和URI模板变量风格可混用。
@RequestMapping(value="/get/id/**/{id}")(4)含正则表达式的一类值
//:可以匹配“/get/123-1”,但不能匹配“/get/abc-1”,这样可以设计更加严格的规则
@RequestMapping(value="/get/{idPre:\\d+}-{idNum:\\d+}")
//可以通过@PathVariable 注解提取路径中的变量(idPre,idNum)(5)或关系
//即 /getAll或/fetchAll都会映射到该方法上。
@RequestMapping(value={"/getAll","/fetchAll"} )method:指定请求的 method 类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等;
@RequestMapping(value=”/get/{bookid}”,method={RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST})
params:指定 request 中必须包含某些参数值时才让该方法处理。
//请求参数包含“action=del”,如:http://localhost:8080/book?action=del
@RequestMapping(params="action=del")
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/owners/{ownerId}")
public class RelativePathUriTemplateController {
//仅处理请求中包含了名为“myParam”,值为“myValue”的请求。
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET, params="myParam=myValue")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}
}headers:指定 request 中必须包含某些指定的 header 值,才能让该方法处理请求。
@RequestMapping(value=”/header/id”, headers = “Accept=application/json”):表示请求的 URL 必须为“/header/id 且请求头中必须有“Accept =application/json”参数即可匹配。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/owners/{ownerId}")
public class RelativePathUriTemplateController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets", method = RequestMethod.GET, headers="Referer=http://www.ifeng.com/")
public void findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}
}仅处理 request 的 header 中包含了指定“Refer”请求头和对应值为“[http://www.ifeng.com/](http://www.ifeng.com/)”的请求。
consumes:指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如 application/json, text/html。
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets", method = RequestMethod.POST, consumes="application/json")
public void addPet(@RequestBody Pet pet, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}方法仅处理 request Content-Type 为“application/json”类型的请求。
produces: 指定返回的内容类型,仅当 request 请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回。
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets/{petId}", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces="application/json")
@ResponseBody
public Pet getPet(@PathVariable String petId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}方法仅处理 request 请求中 Accept 头中包含了”application/json”的请求,同时暗示了返回的内容类型为 application/json;
@RequestParam
@RequestParam 注解用于将方法的参数与 Web 请求的传递的参数进行绑定。使用@RequestParam 可以轻松的访问 HTTP 请求参数的值。
下面是使用该注解的代码示例:
public String requestparam1(@RequestParam String username)请求中包含 username 参数(如/requestparam1?username=zhang)
@RequestParam 有以下三个参数:
value:参数名字,即入参的请求参数名字,如 username 表示 URL 请求的参数名,如果方法中参数名和 URL 请求参数名相同,value 可以省略
required:是否必须,默认是 true,表示请求中一定要有相应的参数,否则将抛出异常;
defaultValue:默认值,表示如果请求中没有同名参数时的默认值,设置该参数时,自动将 required 设为 false。
public String requestparam4(@RequestParam(value="username",required=false) String username)表示请求中可以没有名字为 username 的参数,如果没有默认为 null,此处需要注意如下几点:
原子类型:必须有值,否则抛出异常,如果允许空值请使用包装类代替。
Boolean 包装类型:默认 Boolean.FALSE,其他引用类型默认为 null。
如果请求中有多个同名的应该如何接收呢?如给用户授权时,可能授予多个权限,首先看下如下代码:
public String requestparam7(@RequestParam(value="role") String roleList)如果请求参数类似于url?role=admin&rule=user,则实际 roleList 参数入参的数据为“admin,user”,即多个数据之间使用 “,” 分割;
我们最好使用一个字符串数组或列表来接收多个请求参数:
public String requestparam7(@RequestParam(value="role") String[] roleList)或者
public String requestparam8(@RequestParam(value="list") List<String> list)@PathVariable
@PathVariable 注解是将方法中的参数绑定到请求 URI 中的模板变量上。可以通过@RequestMapping 注解来指定 URI 的模板变量,然后使用@PathVariable 注解将方法中的参数绑定到模板变量上。
特别地,@PathVariable 注解允许我们使用 value 或 name 属性来给参数取一个别名。下面是使用此注解的一个示例:
@RequestMapping(value="/users/{userId}/topics/{topicId}")
public String test(
@PathVariable(value="userId") int userId,
@PathVariable(value="topicId") int topicId){
...
}比如请求的 URL 为 “/users/123/topics/456”,则自动将 URL 中模板变量{userId}和{topicId}绑定到通过@PathVariable 注解的同名参数上,
即入参后 userId=123、topicId=456。
模板变量名需要使用{ }进行包裹,如果方法的参数名与 URI 模板变量名一致,则在@PathVariable 中就可以省略别名的定义。
提示:如果参数是一个非必须的,可选的项,则可以在@PathVariable 中设置 require = false
_@_ModelAttribute
ModelAttribute 可以应用在方法参数上或方法上,他的作用主要是当注解在方法参数上时会将注解的参数对象添加到 Model 中;当注解在
请求处理方法 Action 上时会将该方法变成一个非请求处理的方法,但其它 Action 被调用时会首先调用该方法。
6.1 @ModelAttribute 注释一个方法
被@ModelAttribute 注释的方法表示这个方法的目的是增加一个或多个模型(model)属性。这个方法和被@RequestMapping 注释的方法
一样也支持@RequestParam 参数,但是它不能直接被请求映射。实际上,控制器中的@ModelAttribute 方法是在同一控制器中的
@RequestMapping 方法被调用之前调用的。
被@ModelAttribute 注释的方法用于填充 model 属性,例如,为下拉菜单填充内容,或检索一个 command 对象(如,Account),用它
来表示一个 HTML 表单中的数据。
一个控制器可以有任意数量的@ModelAttribute 方法。所有这些方法都在@RequestMapping 方法被调用之前调用。
有两种类型的@ModelAttribute 方法。一种是:只加入一个属性,用方法的返回类型隐含表示。另一种是:方法接受一个 Model 类型的参
数,这个 model 可以加入任意多个 model 属性。
(1)@ModelAttribute 注释 void 返回值的方法
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test")
public class TestController {
/**
* 1.@ModelAttribute注释void返回值的方法
* @param abc
* @param model
*/
@ModelAttribute
public void populateModel(@RequestParam String abc, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("attributeName", abc);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld() {
return "test/helloWorld";
}
}这个例子,在获得请求/helloWorld 后,populateModel 方法在 helloWorld 方法之前先被调用,它把请求参数(/helloWorld?abc=text)
加入到一个名为 attributeName 的 model 属性中,在它执行后 helloWorld 被调用,返回视图名 helloWorld 和 model 已由_@_ModelAttribute
方法生产好了。这个例子中 model 属性名称和 model 属性对象由 model.addAttribute()实现,不过前提是要在方法中加入一个 Model 类型
的参数。
(2)@ModelAttribute 注释返回具体类的方法
@ModelAttribute
public User getUserInfo(String id){
if(id!=null && !id.equals("")){
return userService.getUserInfo(id);
}
return null;
}这种情况,model 属性的名称没有指定,它由返回类型隐含表示,如这个方法返回 User 类型,那么这个 model 属性的名称是 user。
这个例子中 model 属性名称有返回对象类型隐含表示,model 属性对象就是方法的返回值。它无须要特定的参数。
(3)@ModelAttribute(value=””)注释返回具体类的方法
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test")
public class TestController {
/**
* 3.@ModelAttribute(value="")注释返回具体类的方法
* @param abc
* @return
*/
@ModelAttribute("str")
public String getParam(@RequestParam String param) {
return param;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld() {
return "test/helloWorld";
}
}这个例子中使用@ModelAttribute 注释的 value 属性,来指定 model 属性的名称。model 属性对象就是方法的返回值。它无须要特定的参数。
完整的代码:
package demo.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import demo.model.User;
import demo.service.IUserService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
/**
* 1.@ModelAttribute注释void返回值的方法
* @param abc
* @param model
*/
@ModelAttribute
public void populateModel(@RequestParam String abc, Model model) {
model.addAttribute("attributeName", abc);
}
/**
* 2.@ModelAttribute注释返回具体类的方法
* @param id
* @return
*/
@ModelAttribute
public User getUserInfo(String id){
if(id!=null && !id.equals("")){
return userService.getUserInfo(id);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 3.@ModelAttribute(value="")注释返回具体类的方法
* @param abc
* @return
*/
@ModelAttribute("str")
public String getParam(@RequestParam String param) {
return param;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloWorld")
public String helloWorld() {
return "test/helloWorld";
}
}Jsp 前台取值:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>helloWorld</title>
</head>
<body>
1.The attributeValue is: ${attributeName}
<br/><br/>
2.用户信息:<br/>
姓名:${user.user_name}<br/>
年龄:${user.user_age}<br/>
邮箱:${user.user_email}<br/><br/>
3.The param is: ${str}
</body>
</html>页面效果图:
URL 格式:http://localhost/SSMDemo/test/helloWorld?abc=text&id=1¶m=aaa 注:当 url 或者 post 中不包含参数 abc 和参数 param 时,会报错。
(4)@ModelAttribute 和@RequestMapping 同时注释一个方法
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloWorld")
@ModelAttribute("attributeName")
public String helloWorld() {
return "hi";
}
}这时这个方法的返回值并不是表示一个视图名称,而是 model 属性的值,视图名称由 RequestToViewNameTranslator 根据请求”/helloWorld”转换为 helloWorld。Model 属性名称由@ModelAttribute(value=””)指定,相当于在 request 中封装了 key=attributeName,value=hi。
Jsp 页面:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>helloWorld</title>
</head>
<body>
The attributeValue is: ${attributeName}
</body>
</html>4.2 @ModelAttribute 注释一个方法的参数
@ModelAttribute 注释方法的一个参数表示应从模型 model 中取得。若在 model 中未找到,那么这个参数将先被实例化后加入到 model 中。若在 model 中找到,则请求参数名称和 model 属性字段若相匹配就会自动填充。这个机制对于表单提交数据绑定到对象属性上很有效。
当@ModelAttribute 注解用于方法参数时,它有了双重功能,即“存/取”。首先,它从模型中取出数据并赋予对应的参数,如果模型中尚不存在,则实例化一个,并存放于模型中;其次,一旦模型中已存在此数据对象,接下来一个很重要的步骤便是将请求参数绑定到此对象上(请求参数名映射对象属性名),这是 Spring MVC 提供的一个非常便利的机制–数据绑定。
@RequestMapping(value = "/login.htm", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String doLogin(@ModelAttribute("baseMember") BaseMember member) {
member.setLoginName("loginName");
return "home";
}上述代码中,如果模型中尚不存在键名为“baseMember”的数据,则首先会调用 BaseMember 类的默认构造器创建一个对象,如果不存在默认构造器会抛出异常。因此,给实体类提供一个默认构造器是一个好的编程习惯。当请求路径的请求参数或提交的表单与 BaseMember 的属性名匹配时,将自动将其值绑定到 baseMember 对象中,非常的便利!这可能是我们使用@ModelAttribute 最主要的原因之一。比如:请求路径为http://localhost:8080/spring-web/login.htm?loginName=myLoginName,baseMember 对象中的 loginName 属性的值将被设置为 myLoginName。
4.3 @ModelAttribute 注解的使用场景
当@ModelAttribute 注解用于方法时,与其处于同一个处理类的所有请求方法执行前都会执行一次此方法,这可能并不是我们想要的,因
此,我们使用更多的是将其应用在请求方法的参数上,而它的一部分功能与@RequestParam 注解是一致的,只不过@RequestParam 用
于绑定单个参数值,而@ModelAttribute 注解可以绑定所有名称匹配的,此外它自动将绑定后的数据添加到模型中,无形中也给我们提供
了便利,这也可能是它命名为 ModelAttribute 的原因。
@SessionAttributes
在默认情况下,ModelMap 中的属性作用域是 request 级别,也就是说,当本次请求结束后,ModelMap 中的属性将销毁。如果希望在多个请求中共享 ModelMap 中的属性,必须将其属性转存到 session 中,这样 ModelMap 的属性才可以被跨请求访问。
Spring 允许我们有选择地指定 ModelMap 中的哪些属性需要转存到 session 中,以便下一个请求属对应的 ModelMap 的属性列表中还能访问到这些属性。这一功能是通过类定义处标注 _@_SessionAttributes 注解来实现的。
package demo.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.SessionAttributes;
import demo.model.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/demo1")
//(1)将ModelMap中属性名为currUser的属性放到Session属性列表中,以便这个属性可以跨请求访问
@SessionAttributes("currUser")
public class Demo1Controller {
@RequestMapping(value="/getUser")
public String getUser(ModelMap model){
User user=new User();
user.setUser_name("zhangsan");
user.setUser_age(25);
user.setUser_email("zhangsan@sina.com");
//(2)向ModelMap中添加一个属性
model.addAttribute("currUser",user);
return "/demo/user";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/getUser1")
public String getUser1(ModelMap model){
User user=(User)model.get("currUser");
System.out.println(user.getUser_name());
System.out.println(user.getUser_age());
System.out.println(user.getUser_email());
return "demo/user1";
}
}我们在(2)处添加了一个 ModelMap 属性,其属性名为 currUser,而(1)处通过 _@_SessionAttributes 注解将 ModelMap 中名为 currUser 的属性放置到 Session 中,所以我们不但可以在 getUser() 请求所对应的 JSP 视图页面中通过 request.getAttribute(“currUser”) 和 session.getAttribute(“currUser”) 获取 user 对象,还可以在下一个请求(getUser1())所对应的 JSP 视图页面中通过 session.getAttribute(“currUser”) 或 session.getAttribute(“currUser”)访问到这个属性。
这里我们仅将一个 ModelMap 的属性放入 Session 中,其实 _@_SessionAttributes 允许指定多个属性。你可以通过字符串数组的方式指定多个属性,如 @SessionAttributes({“attr1”,”attr2”})。此外,_@_SessionAttributes 还可以通过属性类型指定要 session 化的 ModelMap 属性,如 _@_SessionAttributes(types = User.class),当然也可以指定多个类,如 _@_SessionAttributes(types = {User.class,Dept.class}),还可以联合使用属性名和属性类型指定:_@_SessionAttributes(types = {User.class,Dept.class},value={“attr1”,”attr2”})。
user.jsp 页面:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<%@ page import="demo.model.User" %>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title>
</head>
<body><br>
<%User user=(User)session.getAttribute("currUser");%>
用户名:<%=user.getUser_name() %><br/>
年龄:<%=user.getUser_age() %><br/>
邮箱:<%=user.getUser_email() %><br/><br/>
<a href="<%=path %>/demo1/getUser1">跳转</a>
</body>
</html>通过@ModelAttribute 绑定
**_@_SessionAttributes **** 是用来在 controller 内部共享 model 属性的。 **我们可以在需要访问 Session 属性的 controller 上加上 @SessionAttributes,然后在 action 需要的 User 参数上加上 @ModelAttribute,并保证两者的属性名称一致。SpringMVC 就会自动将 _@_SessionAttributes 定义的属性注入到 ModelMap 对象,在 setup action 的参数列表时,去 ModelMap 中取到这样的对象,再添加到参数列表。只要我们不去调用 SessionStatus 的 setComplete() 方法,这个对象就会一直保留在 Session 中,从而实现 Session 信息的共享。
@Controller
@SessionAttributes("currentUser")
public class GreetingController{
@RequestMapping
public void hello(@ModelAttribute("currentUser") User user){
//user.sayHello()
}
}@SessionAttributes 清除
@SessionAttributes 需要清除时,使用 SessionStatus.setComplete();来清除。注意,它只清除@SessionAttributes 的 session,不会清除 HttpSession 的数据。故如用户身份验证对象的 session 一般不用它来实现,还是用 session.setAttribute 等传统的方式实现。
@Responsebody 与_@_RequestBody
@Responsebody 表示该方法的返回结果直接写入 HTTP response body 中。一般在异步获取数据时使用,在使用@RequestMapping 后,返回值通常解析为跳转路径,加上@Responsebody 后返回结果不会被解析为跳转路径,而是封装成一个 JSON 对象返回给前端浏览器。
@RequestBody 在处理请求方法的参数列表中使用,它可以将请求主体中的参数绑定到一个对象中,请求主体参数是通过 HttpMessageConverter 传递的,根据请求主体中的参数名与对象的属性名进行匹配并绑定值。此外,还可以通过@Valid 注解对请求主体中的参数进行校验。
下面是一个使用@RequestBody 的示例:
下面是一个前后端分离的 ajax 请求响应过程:
$("#btn2").click(function () {
var url = "<%=request.getContextPath()%>/User/addUserInfo";
var data = {
user_name: $("#userName").val(),
user_sex: $("#userSex").val(),
user_age: $("#userAge").val(),
user_email: $("#userEmail").val(),
user_telephone: $("#userTelephone").val(),
user_education: $("#userEducation").val(),
user_title: $("#userTitle").val(),
};
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
contentType: "application/json",
url: url,
dataType: "json",
data: JSON.stringify(data),
async: false,
success: function (data) {
alert("新增成功!");
},
error: function (XMLHttpRequest, textStatus, errorThrown) {
alert(XMLHttpRequest.status);
alert(XMLHttpRequest.readyState);
alert(textStatus);
},
});
});java 代码
@RequestMapping(value="/addUserInfo",method=RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
//将请求中的data写入UserModel对象中
public String addUserInfo(@RequestBody UserModel user){
//不会被解析为跳转路径,而是直接写入HTTP response body中
return "{}";
}比较:**_@_RequestBody **和 **_@_ResponseBody **** **
**_@_RequestBody **** **
作用:
i) 该注解用于读取 Request 请求的 body 部分数据,使用系统默认配置的HttpMessageConverter进行解析,然后把相应的数据绑定到要返回的对象上;
ii) 再把 HttpMessageConverter 返回的对象数据绑定到 controller 中方法的参数上。
使用时机:
A) GET、POST 方式提时, 根据 request header Content-Type 的值来判断:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 可选(即非必须,因为这种情况的数据@RequestParam, @ModelAttribute 也可以处理,当然@RequestBody 也能处理);
multipart/form-data, 不能处理(即使用@RequestBody 不能处理这种格式的数据);
其他格式, 必须(其他格式包括 application/json, application/xml 等。这些格式的数据,必须使用@RequestBody 来处理);
B) PUT 方式提交时, 根据 request header Content-Type 的值来判断:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 必须;
multipart/form-data, 不能处理;
其他格式, 必须;
说明:request 的 body 部分的数据编码格式由 header 部分的 Content-Type 指定;
**_@_ResponseBody **** 将内容或对象作为 HTTP 响应正文返回,并调用适合 HttpMessageConverter 的 Adapter 转换对象,写入输出流。 **
作用:
该注解用于将 Controller 的方法返回的对象,通过适当的 HttpMessageConverter 转换为指定格式后,写入到 Response 对象的 body 数据区。
使用时机:
返回的数据不是 html 标签的页面,而是其他某种格式的数据时(如 json、xml 等)使用;
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice 是@Component 注解的一个延伸注解,Spring 会自动扫描并检测被@ControllerAdvice 所标注的类。
@ControllerAdvice 需要和@ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder 以及@ModelAttribute 注解搭配使用,主要是用来处理控制器所抛出的异常信息。
首先,我们需要定义一个被@ControllerAdvice 所标注的类,在该类中,定义一个用于处理具体异常的方法,并使用@ExceptionHandler 注解进行标记。
此外,在有必要的时候,可以使用@InitBinder 在类中进行全局的配置,还可以使用@ModelAttribute 配置与视图相关的参数。使用@ControllerAdvice 注解,就可以快速的创建统一的,自定义的异常处理类。
下面是一个使用@ControllerAdvice 的示例代码:
@CrossOrigin
@CrossOrigin 注解将为请求处理类或请求处理方法提供跨域调用支持。如果我们将此注解标注类,那么类中的所有方法都将获得支持跨域的能力。使用此注解的好处是可以微调跨域行为。使用此注解的示例如下:
@InitBinder
@InitBinder 注解用于标注初始化WebDataBinider的方法,该方法用于对 Http 请求传递的表单数据进行处理,如时间格式化、字符串处理等。
下面是使用此注解的示例:
Spring Bean 注解
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan 注解用于配置 Spring 需要扫描的被组件注解注释的类所在的包。可以通过配置其 basePackages 属性或者 value 属性来配置需要扫描的包路径。value 属性是 basePackages 的别名。此注解的用法如下:
@Component
@Component 注解用于标注一个普通的组件类,它没有明确的业务范围,只是通知 Spring 被此注解的类 注入到 Spring IOC 容器中并进行管理。
@Service
@Service 注解是@Component 的一个延伸(特例),它用于标注业务逻辑类。与@Component 注解一样,被此注解标注的类,会自动被 Spring 所管理。下面是使用@Service 注解的示例:
@Repository
@Repository 注解也是@Component 注解的延伸,与@Component 注解一样,被此注解标注的类会被 Spring 自动管理起来,@Repository 注解用于标注 DAO 层的数据持久化类。此注解的用法如下:
@DependsOn
@DependsOn 注解可以配置 Spring IoC 容器在初始化一个 Bean 之前,先初始化其他的 Bean 对象。下面是此注解使用示例代码:
@Bean
@Bean 注解主要的作用是告知 Spring,被此注解所标注的类将需要纳入到 Bean 管理工厂中。@Bean 注解的用法很简单,在这里,着重介绍@Bean 注解中 initMethod 和 destroyMethod 的用法。示例如下:
@Scope
@Scope 注解可以用来定义@Component 标注的类的作用范围以及@Bean 所标记的类的作用范围。
@Scope 所限定的作用范围有:singleton、prototype、request、session、globalSession 或者其他的自定义范围。这里以 prototype 为例子进行讲解。
当一个 Spring Bean 被声明为 prototype(原型模式)时,在每次需要使用到该类的时候,Spring IoC 容器都会初始化一个新的改类的实例。在定义一个 Bea 时,可以设置 Bean 的 scope 属性为 prototype:scope="prototype",也可以使用@Scope 注解设置,如下:
@Scope(value=ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROPTOTYPE)
下面将给出两种不同的方式来使用@Scope 注解,示例代码如下:

当@Scope 的作用范围设置成 Singleton 时,被此注解所标注的类只会被 Spring IoC 容器初始化一次。在默认情况下,Spring IoC 容器所初始化的类实例都为 singleton。同样的原理,此情形也有两种配置方式,示例代码如下:
@Autowired
@Autowired 注解用于标记 Spring 将要解析和注入的依赖项。此注解可以作用在构造函数、字段和 setter 方法上。
首先要知道另一个东西,default-autowire,它是在 xml 文件中进行配置的,可以设置为 byName、byType、constructor 和 autodetect;比如 byName,不用显式的在 bean 中写出依赖的对象,它会自动的匹配其它 bean 中 id 名与本 bean 的 set**相同的,并自动装载。
@Autowired 是用在 JavaBean 中的注解,通过 byType 形式,用来给指定的字段或方法注入所需的外部资源。两者的功能是一样的,就是能减少或者消除属性或构造器参数的设置,只是配置地方不一样而已。
默认情况下,@Autowired 注解意味着依赖是必须的,它类似于 @Required 注解,然而,你可以使用 @Autowired 的 (required=false) 选项关闭默认行为。
autowire 四种模式的区别:
@Autowired 作用在 setter 方法上
你可以在 JavaBean中的 setter 方法中使用 @Autowired 注解。当 Spring 遇到一个在 setter 方法中使用的 @Autowired 注解,它会在方法中执行 byType 自动装配。
@Autowired 作用于字段上
你可以在属性中使用 @Autowired 注解来除去 setter 方法。当时使用 为自动连接属性传递的时候,Spring 会将这些传递过来的值或者引用自动分配给那些属性。所以利用在属性中 @Autowired 的用法,你的 TextEditor.java 文件将变成如下所示:
@Autowired 作用于构造函数
下面是@Autowired 注解标注构造函数的使用示例:
@Primary
当系统中需要配置多个具有相同类型的 bean 时,@Primary 可以定义这些 Bean 的优先级。下面将给出一个实例代码来说明这一特性:
输出结果:
this is send DingDing method message.
@PostConstruct 与@PreDestroy
值得注意的是,这两个注解不属于 Spring,它们是源于 JSR-250 中的两个注解,位于 common-annotations.jar 中。@PostConstruct 注解用于标注在 Bean 被 Spring 初始化之前需要执行的方法。@PreDestroy 注解用于标注 Bean 被销毁前需要执行的方法。下面是具体的示例代码:
@Qualifier
当系统中存在同一类型的多个 Bean 时,@Autowired 在进行依赖注入的时候就不知道该选择哪一个实现类进行注入。此时,我们可以使用@Qualifier 注解来微调,帮助@Autowired 选择正确的依赖项。下面是一个关于此注解的代码示例:
Spring Boot 注解
@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication 注解是一个组合注解,在被它标注的类中,可以定义一个或多个 Bean,并自动触发自动配置 Bean 和自动扫描组件。此注解相当于@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration 和@ComponentScan 的组合。
此注解标注的类就是在 Spring Boot 应用程序的启动类中,run 方法就是 springboot 程序入口。示例代码如下:
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解用于通知 Spring,根据当前类路径下引入的依赖包,自动配置与这些依赖包相关的配置项。
@ConditionalOnClass 与@ConditionalOnMissingClass
这两个注解属于类条件注解,它们根据是否存在某个类作为判断依据来决定是否要执行某些配置。下面是一个简单的示例代码:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DataSource.class)
class MySQLAutoConfiguration {
//...
}@ConditionalOnBean 与@ConditionalOnMissingBean
这两个注解属于对象条件注解,根据是否存在某个对象作为依据来决定是否要执行某些配置方法。示例代码如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(name="dataSource")
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(){
//...
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MyBean myBean(){
//...
}@ConditionalOnProperty
@ConditionalOnProperty 注解会根据 Spring 配置文件中的配置项是否满足配置要求,从而决定是否要执行被其标注的方法。示例代码如下:
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name="alipay",havingValue="on")
Alipay alipay(){
return new Alipay();
}@ConditionalOnResource
此注解用于检测当某个配置文件存在使,则触发被其标注的方法,下面是使用此注解的代码示例:
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "classpath:website.properties")
Properties addWebsiteProperties(){
//...
}@ConditionalOnWebApplication 与@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
这两个注解用于判断当前的应用程序是否是 Web 应用程序。如果当前应用是 Web 应用程序,则使用 Spring WebApplicationContext,并定义其会话的生命周期。下面是一个简单的示例:
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
HealthCheckController healthCheckController(){
//...
}@ConditionalExpression
此注解可以让我们控制更细粒度的基于表达式的配置条件限制。当表达式满足某个条件或者表达式为真的时候,将会执行被此注解标注的方法。
@Bean
@ConditionalException("${localstore} && ${local == 'true'}")
LocalFileStore store(){
//...
}@Conditional
@Conditional 注解可以控制更为复杂的配置条件。在 Spring 内置的条件控制注解不满足应用需求的时候,可以使用此注解定义自定义的控制条件,以达到自定义的要求。下面是使用该注解的简单示例:
@Conditioanl(CustomConditioanl.class)
CustomProperties addCustomProperties(){
//...
}重点掌握注解的原理
条件注解@Conditional
条件注解并非一个新事物,这是一个存在于 Spring 中的东西,我们在 Spring 中常用的 profile 实际上就是条件注解的一个特殊化。
条件注解可以说条件注解是整个 Spring Boot 的基石,它存在于源码的方方面面,
想要把 Spring Boot 的原理搞清,条件注解必须要会用。
Spring4 中提供了更加通用的条件注解,让我们可以在满足不同条件时创建不同的 Bean,这种配置方式在 Spring Boot 中得到了广泛的使用,大量的自动化配置都是通过条件注解来实现的,
有的小伙伴可能没用过条件注解,但是开发环境、生产环境切换的 Profile 多多少少都有用过吧?实际上这就是条件注解的一个特例。
基本原理
来看一个 Demo 吧,步骤如下:
//1、定义一个 Food 接口:
public interface Food {
String showName();
}
//2、Food 接口有一个 showName 方法和两个实现类:
public class Rice implements Food {
public String showName() {
return "米饭";
}
}
public class Noodles implements Food {
public String showName() {
return "面条";
}
}
/*3、
分别是 Rice 和 Noodles 两个类,两个类实现了 showName 方法,然后分别返回不同值。
接下来再分别创建 Rice 和 Noodles 的条件类,如下:
*/
public class NoodlesCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("people").equals("北方人");
}
}
public class RiceCondition implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
return context.getEnvironment().getProperty("people").equals("南方人");
}
}
/*4、
在 matches 方法中做条件属性判断,当系统属性中的 people 属性值为 ‘北方人’ 的时候,NoodlesCondition 的条件得到满足,
当系统中 people 属性值为 ‘南方人’ 的时候,RiceCondition 的条件得到满足,
换句话说,哪个条件得到满足,一会就会创建哪个 Bean 。接下来我们来配置 Rice 和 Noodles :
*/
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean("food")
@Conditional(RiceCondition.class)
Food rice() {
return new Rice();
}
@Bean("food")
@Conditional(NoodlesCondition.class)
Food noodles() {
return new Noodles();
}
}这个配置类,大家重点注意两个地方:
- 两个 Bean 的名字都为 food,这不是巧合,而是有意取的。两个 Bean 的返回值都为其父类对 Food。
- 每个 Bean 上都多了 @Conditional 注解,当 @Conditional 注解中配置的条件类的 matches 方法返回值为 true 时,对应的 Bean 就会生效。
配置完成后,我们就可以在 main 方法中进行测试了:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties().put("people", "南方人");
ctx.register(JavaConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
Food food = (Food) ctx.getBean("food");
System.out.println(food.showName());
}
}首先我们创建一个 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 实例用来加载 Java 配置类,然后我们添加一个 property 到 environment 中,添加完成后,再去注册我们的配置类,然后刷新容器。容器刷新完成后,我们就可以从容器中去获取 food 的实例了,这个实例会根据 people 属性的不同,而创建出来不同的 Food 实例。
这个就是 Spring 中的条件注解。
进阶-@Profile
条件注解还有一个进化版,那就是 Profile。我们一般利用 Profile 来实现在开发环境和生产环境之间进行快速切换。其实 Profile 就是利用条件注解来实现的。
还是刚才的例子,我们用 Profile 来稍微改造一下:
首先 Food、Rice 以及 Noodles 的定义不用变,条件注解这次我们不需要了,我们直接在 Bean 定义时添加 @Profile 注解,如下:
@Configuration
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean("food")
@Profile("南方人")
Food rice() {
return new Rice();
}
@Bean("food")
@Profile("北方人")
Food noodles() {
return new Noodles();
}
}这次不需要条件注解了,取而代之的是 @Profile 。然后在 Main 方法中,按照如下方式加载 Bean:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("南方人");
ctx.register(JavaConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
Food food = (Food) ctx.getBean("food");
System.out.println(food.showName());
}
}效果和上面的案例一样。
这样看起来 @Profile 注解貌似比 @Conditional 注解还要方便,那么 @Profile 注解到底是什么实现的呢?
我们来看一下 @Profile 的定义:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(ProfileCondition.class)
public @interface Profile {
String[] value();
}可以看到,它也是通过条件注解来实现的。条件类是 ProfileCondition ,我们来看看:
class ProfileCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(Profile.class.getName());
if (attrs != null) {
for (Object value : attrs.get("value")) {
if (context.getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(Profiles.of((String[]) value))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
}看到这里就明白了,其实还是我们在条件注解中写的那一套东西,只不过 @Profile 注解自动帮我们实现了而已。
@Profile 虽然方便,但是不够灵活,因为具体的判断逻辑不是我们自己实现的。而 @Conditional 则比较灵活。
总结:
两个例子向大家展示了条件注解在 Spring 中的使用,它的一个核心思想就是当满足某种条件的时候,某个 Bean 才会生效,而正是这一特性,支撑起了 Spring Boot 的自动化配置。
@Import
SpringBoot 集成 Redis 缓存
http://www.bjpowernode.com/tutorial_springboot/831.html
#配置pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
#核心配置文件
#配置redis连接信息(单机模式)
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379service 文件
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public RespBean getAllStudent() {
List<TStudent> studentList = null;
Object arr = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("studentList");
System.out.println(arr);
if(ObjectUtils.isEmpty(arr) || arr == null || arr == "null"){
System.out.println("===============>查询数据库");
studentList = studentMapper.selectList(null);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("studentList", JSON.toJSONString(studentList),15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return RespBean.ok("ok",studentList);
}
System.out.println("===============>从redis缓存中取值");
return RespBean.ok("ok",JSON.parse((String)arr));
}SpringBoot 集成 Dubbo
http://www.bjpowernode.com/tutorial_springboot/832.html
获取 Spring 容器并自动执行
1、SpringApplication.run()方法返回的 Spring 容器对象

代码:
@SpringBootApplication
public class NotwebappApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式一:SpringApplication.run()方法返回的ConfigurableApplicationContext是Spring容器的实现类
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(NotwebappApplication.class, args);
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) context.getBean("studentServiceImpl");
String ss = studentService.sayHello();
System.out.println(ss);
}
}ConfigurableApplicationContext.java 关系图
2、Springboot 的入口类实现 CommandLineRunner 接口
@SpringBootApplication
public class NotwebappApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
//第二步:通过容器获取bean,并注入给userService
@Autowired
public StudentService studentService;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一步:SpringBoot的启动程序,会初始化spring容器
SpringApplication.run(NotwebappApplication.class, args);
}
//覆盖接口中的run方法
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
//第三步:容器启动后调用run方法,在该方法中调用业务方法
String s = studentService.sayHello();
System.out.println(s);
}
}SpringBoot 使用拦截器
参考:http://www.bjpowernode.com/tutorial_springboot/838.html
1、实现一个拦截器(实现 HandlerInterceptor)
public class MyInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行MyInterceptor.preHandle==============>");
HashMap<String, String> loginUser = (HashMap<String, String>) request.getSession().getAttribute("login_user");
if(ObjectUtils.isEmpty(loginUser)){
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath()+"/springboot/login");
//被拦截
return false;
}else{
//通过
return true;
}
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行MyInterceptor.postHandle--------------->");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行MyInterceptor.afterCompletion++++++++++++++++++++++++>");
}
}2、通过配置类注册拦截器
在项目中创建一个 config 包,创建一个配置类 InterceptorConfig,并实现 WebMvcConfigurer 接口, 覆盖接口中的 addInterceptors 方法,并为该配置类添加@Configuration 注解,标注此类为一个配置类,让 Spring Boot 扫描到,这里的操作就相当于 SpringMVC 的注册拦截器 ,@Configuration 就相当于一个 applicationContext-mvc.xml。
@Configuration
public class InterceptorConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//定义需要拦截的路径
String [] addPathPatterns = {
"/springboot/**"
};
//定义不需要拦截的路径
String [] excludePathPatterns = {
"/test/**",
"/springboot/login",
"/springboot/doLogin",
"/springboot/register",
"/springboot/doRegister",
};
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor())
.addPathPatterns(addPathPatterns)
.excludePathPatterns(excludePathPatterns);
}
}3、测试
1)直接输入 http://localhost:8080/springboot/hello 会跳转到登录页面 http://localhost:8080/springboot/login
2)访问 http://localhost:8080/springboot/login
输入用户名密码登录
3)登录成功后再访问 http://localhost:8080/springboot/hello
控制台打印:
执行MyInterceptor.preHandle==============>
执行MyInterceptor.postHandle--------------->
执行MyInterceptor.afterCompletion++++++++++++++++++++++++>SpringBoot 请求转发和重定向
参考:https://www.icode9.com/content-4-825109.html
1、转发
方式一:使用 “forword” 关键字(不是指 java 关键字),注意:类的注解不能使用_@_RestController 要用_@_Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(@PathVariable String name) {
return "forword:/ceng/hello.html";
}方式二:使用 servlet 提供的 API,注意:类的注解可以使用@RestController,也可以使用_@_Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test(@PathVariable String name, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/ceng/hello.html").forward(request,response);
}2、重定向
方式一:使用 “redirect” 关键字(不是指 java 关键字),注意:类的注解不能使用@RestController,要用_@_Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test(@PathVariable String name) {
return "redirect:/ceng/hello.html";
}方式二:使用 servlet 提供的 API,注意:类的注解可以使用@RestController,也可以使用_@_Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test/test01/{name}" , method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test(@PathVariable String name, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.sendRedirect("/ceng/hello.html");
}使用 API 进行重定向时,一般会在 url 之前加上:request.getContextPath()
SpringBoot 整合 Servlet 的两种方式
http://www.bjpowernode.com/tutorial_springboot/839.html
SpringBoot 项目打包
jar 包和 war 包的介绍和区别
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3b5c45e8e5bd
打 jar 包
打 war 包
1、使用 IEDA 创建项目

将打包方式改为 War,会在创建项目时生成 ServletInitializer.java
2、spring-boot-starter-web 去除内嵌的 tomcat 依赖
pom.xml 文件中要去掉 spring-boot-starter-web 内嵌的 tomcat 或者将 tomcat 依赖 scope 改为 provide
<!-- 移除嵌入式tomcat插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 或者-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>3、SpringBootServletInitializer
继承 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer,实现 configure 方法
为什么继承该类,SpringBootServletInitializer 源码注释:
Note that a WebApplicationInitializer is only needed if you are building a war file and
deploying it. If you prefer to run an embedded web server then you won't need this at all.请注意,WebApplicationInitializer 仅在您构建 war 文件并部署它时才需要。如果您更喜欢运行嵌入式 Web 服务器,那么您根本不需要它
启动类代码:
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}方式一、启动类继承 SpringBootServletInitializer 实现 configure:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(Application.class);
}
}方式二、新增加一个类继承 SpringBootServletInitializer 实现 configure:
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
//此处的Application.class为带有@SpringBootApplication注解的启动类
return builder.sources(DemoApplication.class);
}
}4、打包&部署
1、使用 IDEA 的 Maven 打包工具
注意:
使用外部 Tomcat 部署访问的时候,application.properties(或者 application.yml)中配置的
server.port=8888
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot-jsp将失效,请使用 tomcat 的端口,tomcat,webapps 下项目名进行访问。
为了防止应用上下文所导致的项目访问资源加载不到的问题,建议 pom.xml 文件中<build></build>标签下添加<finalName></finalName>标签:
使用 IDEA 的 maven 打包工具会将项目打包生成为: /tragetspringboot-jsp.war
2、将 war 包拷贝到 tomcat 服务器的 webapps 目录下,运行/bin/startup.bat
3、浏览器中输入:
http://localhost:[tomcat 端口]/[war 包名]/jsp/blog/list
http://localhost:8080/springboot-jsp/jsp/blog/list
SpringBoot 集成 jsp
maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--让内嵌tomcat具有解析jsp功能(必须)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--jstl标签库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>2、引⼊ jsp 编译打包插件
<build>
<finalName>springboot_day1</finalName>
<!--引⼊springboot插件 可以正确打包 显示jsp-->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>3、配置视图解析器
#在配置⽂件中引⼊视图解析器
spring:
mvc:
view:
prefix: / # /代表访问项⽬中webapp中⻚⾯
suffix: .jsp截个图看看
4、新建 webapp 目录
在 java resources 同级目录下新建 webapp 目录,将 jsp 文件放在该目录下
浏览器上输入 url 请求:
以上都配置了,浏览器输入 Controller 访问路径还是 404 找不到 jsp 页面怎么回事呢?
答:是 IDEA 自己的问题,可以有如下两种解决方式
- 使⽤插件启动访问 JSP ⻚⾯

- 使⽤ idea 中指定⼯作⽬录启动 访问 JSP(推荐)

测试时发现,每次修改 jsp 文件都要重新启动 springboot 项目,非常麻烦,如何跟 devtools 结合能热启动呢?
(开启 jsp 页面开发模式,修改 jsp 页面无需重启 springboot 应用)
SpringBoot 集成 Shiro
SpringBoot 集成 SpringSecurity
SpringBoot 数据库连接加密处理
虽然项目的源代码配置是在application.properties文件中,但是,如果使用的是明文账密,还是处于不安全状态,一旦泄露,将会造成不可计量的损失,故而使用一个加密来加密必要的信息,使得数据库更安全。
这里使用 jasypt-spring-boot-starter 来处理加密字符。官网详情点击查看。
1、导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.ulisesbocchio/jasypt-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ulisesbocchio</groupId>
<artifactId>jasypt-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
2、生产加密数据
import org.jasypt.util.text.BasicTextEncryptor;
public class EncryptionTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BasicTextEncryptor textEncryptor = new BasicTextEncryptor();
//自定义加密所需的salt(盐值)
textEncryptor.setPassword("salt123456");
//要加密的数据(数据库的用户名或密码,当然你要是想让URL加密,也是可以的)
String username = textEncryptor.encrypt("root");
String password = textEncryptor.encrypt("123456");
System.out.println("username:" + username);
System.out.println("password:" + password);
}
}每次启动生成的数据都不一样,这次启动控制台打印:
username:YxYODHKPIbPtwOBMdLbC7w==
password:RV+Z9VVoDTDZsccOpDsrdw==
Process finished with exit code 03、修改 application.yml 配置
# 数据库四大组件
spring:
datasource:
username: ENC(YxYODHKPIbPtwOBMdLbC7w==)
password: ENC(RV+Z9VVoDTDZsccOpDsrdw==)
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest?characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 默认加密方式PBEWithMD5AndDES,可以更改为PBEWithMD5AndTripleDES,这里我选择的是默认的
jasypt:
encryptor:
password: salt123456 #你自定义的盐值
# algorithm: PBEWithMD5AndTripleDES然后直接启动项目就 OK 了,测试,可以获取到相应的数据。
注意:如果怕盐值也泄露出去,你可以使用命令启动的时候传入进去盐值。
例如:
java -jar -Djasypt.encryptor.password=盐值 xxx.jar完美解决。
SpringBoot 文件上传
上传到本地
https://github.com/BFD2018/xiong-springboot-demos/tree/master/springboot-filesupload
上传到 fastdfs
https://github.com/BFD2018/xiong-springboot-demos/tree/master/springboot-fdfs
上传到 aliyun-oss
https://github.com/BFD2018/xiong-springboot-demos/tree/master/springboot-aliyun
SpringBoot 发送邮件
源码:https://github.com/BFD2018/xiong-springboot-demos/tree/master/springboot-mail
pom.xml 配置
<!--发送邮件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--swagger2 测试页面模板 访问 http://localhost:8080/doc.html-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId>
<artifactId>knife4j-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>swagger2 测试模板效果如下:
knife4j 基本使用参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/Octopus21/article/details/106769722/




